Hello Peeps!
Are you working with SAP HCM and planning to integrate it with SuccessFactors Employee Central (EC)? Then you’ve likely come across the terms PTP and BIB. In this post, we’ll dive deep into these integration models—Point-to-Point (PTP) and Business Integration Builder (BIB)—explaining their differences, advantages, disadvantages, and use cases in SAP ABAP HCM.
✅ What is PTP (Point-to-Point) in SAP ABAP HCM?
PTP, or Point-to-Point, refers to the traditional integration model used to replicate employee data from SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central (EC) to SAP HCM. It employs a straightforward approach to link fields from Employee Central (EC) to SAP HCM infotypes via custom ABAP coding and commonly used middleware platforms, such as SAP PI/PO or Dell Boomi.
🔍 Key Features of PTP in SAP HCM:
Custom-built field mapping logic.
Inflexible and tightly coupled to infotype structures.
Low reusability of code.
Difficult to maintain in large or complex organizations.
Minimal support for dynamic field behavior.
📘 Example: PTP Mapping in SAP HCM
Suppose EC sends the following data:
json
{
"personIdExternal": "100001",
"jobTitle": "SAP ABAP Consultant",
"startDate": "2022-01-01",
"company": "1100"
}In PTP, the ABAP logic hard-codes how this data maps to infotypes, such as:
"abap
* Hard-coded mapping example
MOVE iv_jobTitle TO p0001-stell.
MOVE iv_company TO p0001-werks.The information is directly stored in Infotype 0001, which handles organizational assignment details. Any changes to EC fields or business rules require direct changes in the ABAP code, making it non-scalable and error-prone.
🚀 What is BIB (Business Integration Builder) in SAP ABAP HCM?
BIB, or Business Integration Builder, is the modern and recommended integration framework developed by SAP for EC to SAP HCM replication. It uses configuration-based mapping rather than hardcoded ABAP logic. BIB allows customers to reuse, maintain, and scale their integrations more efficiently.
🔍 Key Features of BIB:
Uses mapping tables (T77SFEC_*) instead of hardcoded logic.
Supports dynamic and reusable mappings.
Built on the decoupled infotype framework.
Easy enhancement using standard BAdIs.
Supports conditional mappings and rule-based field derivation.
Provides better error handling and auditability.
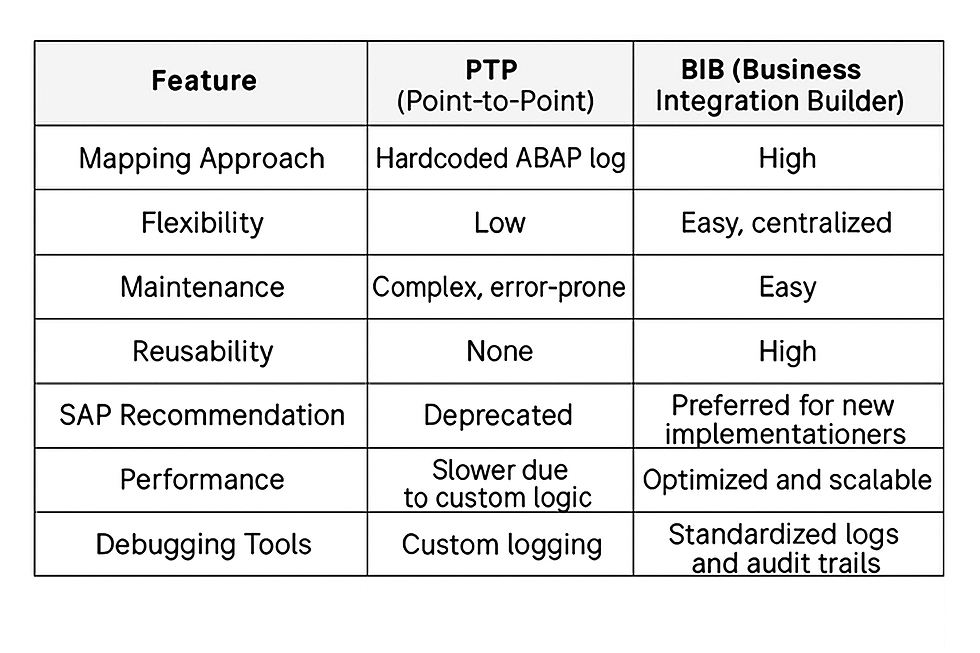
🆚 PTP vs. BIB: Key Differences
📁 Important Tables Used in BIB Integration

🔧 BIB Architecture in SAP ABAP HCM
Here's how the BIB framework works:
Employee Central sends a payload via middleware (SAP CPI, Boomi, etc.).
The SAP HCM system receives the payload using a standard interface (e.g., HRSFEC_PTP_EE_IN).
The BIB framework checks mapping tables for:
Field mapping
Default values
Transformation rules
Executes relevant BAdIs for custom logic:
HRSFEC_B_CE_MASTER_DATA_REPL
HRSFEC_B_CE_PERS_DATA
HRSFEC_B_CE_REPL_VALIDATION
Updates infotypes using the decoupled infotype framework.
💻 Example: BIB Field Mapping
Let’s say EC sends the following field:
json
"company": "1000"In PTP, this would be hardcoded. But in BIB:
The table T77SFEC_BIB_FIELD contains:
EC Field: company
Infotype Field: WERKS (Personnel area)
Target Infotype: 0001
Transformation Rule: Z_MAP_COMPANY_TO_WERKS
This rule can be maintained via table T77SFEC_BIB_RMAP, and transformations happen without modifying ABAP code.
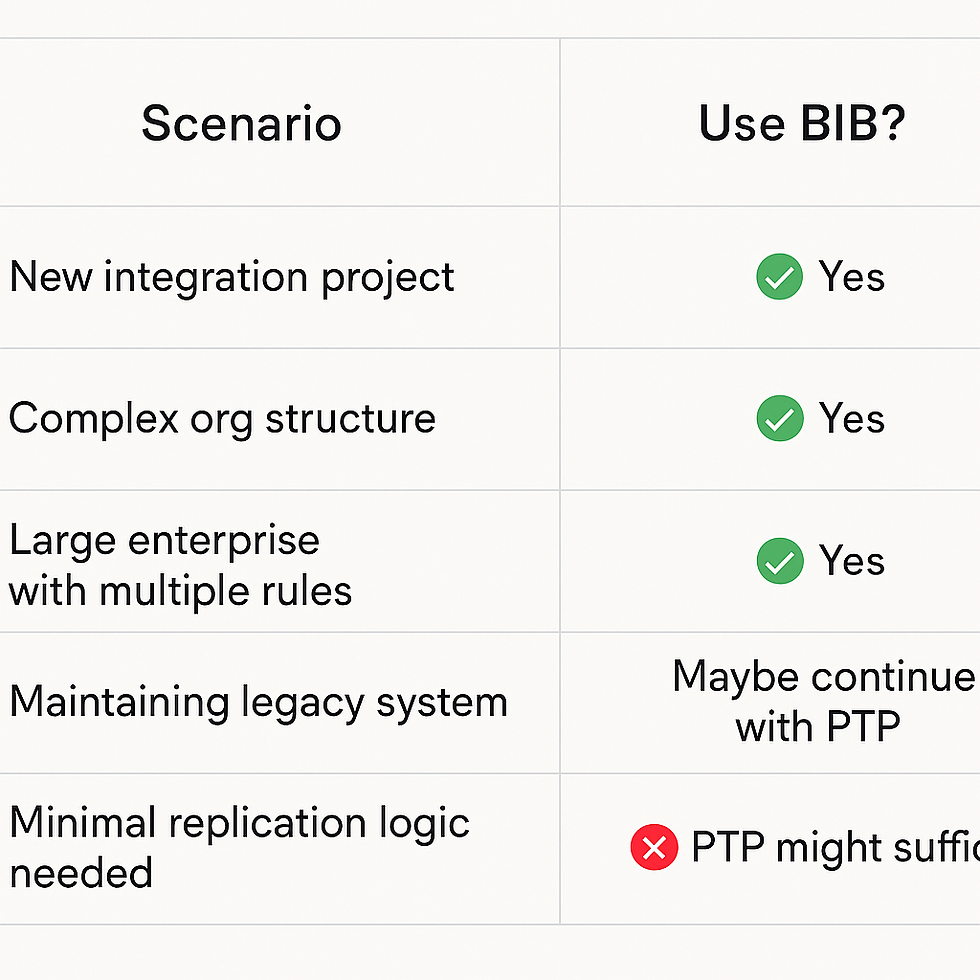
🔁 When to Use BIB Instead of PTP?
🛠️ Enhancements in BIB – BAdIs in Action
You can enhance BIB using the following BAdIs:
HRSFEC_B_CE_MASTER_DATA_REPL: Central BAdI for EC master data replication.
HRSFEC_B_CE_VALIDATION: Add custom validation logic before saving data.
HRSFEC_B_CE_DEFAULTS: Used to assign default values to fields when they are missing from the Employee Central data payload.
HRSFEC_B_CE_MAPPING: Create custom mapping transformations.
Sample BAdI Implementation Snippet:
"abap
METHOD if_ex_hrsfec_b_ce_mapping~map_field.
IF iv_ec_field_name = 'customField1'.
ev_value = 'MappedValue'.
ENDIF.
ENDMETHOD.📊 SAP’s Strategic Direction
SAP is actively promoting BIB and phasing out PTP for EC to HCM integrations. New features and updates from SAP are now focused solely on BIB.
SAP recommends:
“Use BIB as the standard for all new Employee Central to SAP ERP integrations.”
🔒 Challenges with PTP and Why BIB Solves Them
PTP Challenge BIB Solution
Frequent ABAP changes Rule-based mapping tables
Poor documentation Structured configuration
Custom logic duplication Reusable mapping logic
Debugging complexity Standard logs and traceability
Low upgrade compatibility SAP-supported framework
📝 Final Thoughts: Choosing Between PTP and BIB
If you're still using Point-to-Point integrations in your SAP HCM landscape, it's high time to migrate to BIB. Not only is it more maintainable and scalable, but it also aligns with SAP’s long-term integration roadmap.
For developers and functional consultants alike, understanding and implementing BIB is essential for future-proofing your SAP HCM integrations.
🔗 Related Resources
SAP Note 2715856 – BIB Overview
SAP Help: Employee Central Integration
SuccessFactors EC to HCM Integration Guide
📣 Stay Tuned on DrTechSAP
At drtechsap, we cover the latest trends and deep-dive technical articles for SAP ABAP, HCM, SuccessFactors, and more. Subscribe for expert-level blogs, tutorials, and code snippets straight from real-world SAP projects.
Happy Learning!
Dr. Tech
