Hello Peeps!
In this post, we’ll take a closer look at the different types of SAP enhancements and how they work.
Introduction
In the world of SAP development, adapting standard SAP programs to meet business-specific requirements is a common necessity. However, direct modification of standard SAP code is discouraged due to the risks it poses—especially during system upgrades.
That’s where SAP enhancements come into play.
Enhancements allow developers to customize the behavior of standard SAP applications safely and efficiently—without modifying core code. Whether you're working on SAP ECC or the newer S/4HANA, mastering enhancement techniques is essential for every ABAP developer.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn:
What SAP enhancements are
The difference between explicit and implicit enhancements
Main categories include User Exits, Customer Exits, Business Add-Ins (BADIs), and Enhancement Points.
Real-world examples and when to use each
Let’s get started.
🔍 What Are Enhancements in SAP?
Enhancements are mechanisms that allow you to inject custom code into SAP standard applications without altering the original source. They provide a clean, upgrade-safe way to meet business-specific requirements.
SAP offers a wide variety of enhancement techniques, both classic (like User Exits) and modern (like Enhancement Points and BADIs).
Enhancements are essential because they:
Preserve the integrity of SAP standard code
Support system upgrades with minimal conflicts
Allow developers to meet customer-specific needs
Promote modular and maintainable development
🧩 Categories of SAP Enhancements
SAP enhancements are broadly categorized into:
Classic Enhancements
User Exits
Customer Exits
Menu Exits
Screen Exits
Modern Enhancements (Enhancement Framework)
Explicit Enhancements
Implicit Enhancements
BADIs (Business Add-Ins)
Enhancement Spots and Sections
Let’s go deeper into these categories and explain their use cases.
🏗️ Classic Enhancements
1. User Exits
User Exits represent one of the oldest enhancement techniques available in SAP. They are SAP-defined FORM routines embedded in includes, which customers can fill with custom logic.
Available mainly in modules like SD, MM, and FI
Implemented via CMOD/SMOD
Procedural (non-OOP) coding
Often found in programs like MV45AFZZ, MV50AFZ1, etc.
Example Use Case: Validating customer data before saving a sales order.
FORM userexit_save_doc.
IF vbak-zz_cust_field IS INITIAL.
MESSAGE 'Please enter custom field' TYPE 'E'.
ENDIF.
ENDFORM.2. Customer Exits
Customer Exits resemble User Exits but offer a more organized and structured approach. They use function modules prefixed with EXIT_... and are implemented in Z... function groups.
Types of Customer Exits:
Function Module Exits
Menu Exits
Screen Exits
Example Use Case:Adding an extra tab on the customer master screen (Screen Exit) or extending menu options in the ME21N transaction (Menu Exit).
💡 Modern Enhancements: SAP Enhancement Framework
Starting with SAP NetWeaver 7.0, SAP adopted a more flexible and object-oriented strategy through the use of the Enhancement Framework.
This includes:
Explicit Enhancements
Implicit Enhancements
BADIs (Business Add-Ins)
Enhancement Spots and Sections
Let’s break these down.
⚙️ Explicit vs Implicit Enhancements
✅ Explicit Enhancements
These are specific locations within SAP's standard code where developers have intentionally added enhancement hooks for custom logic implementation.
enhacement-point <name>SPOTS<spot_name>.
You can find and implement them using:
Right-click → Enhancement Implementation
Transactions like SE20 or SE80
Advantages:
Easy to identify
Upgrade-safe
Used for both procedural and OO programming
Example:
ENHANCEMENT 1 ZMY_ENHANCEMENT. "Active version
WRITE:'Custom logic here'.
ENDENHANCEMENT.✅ Implicit Enhancements
These are automatically provided by SAP at strategic locations like:
Start and end of FORM routines
Start and end of Function Modules
Start and end of ABAP Methods
End of Reports and Includes
They are not marked explicitly in code but can be accessed via enhancement tools in SE80.
Example Scenario: You want to add custom logic after a standard method executes in a report.
Simply place your cursor at the end of the method and choose: Enhancement Implementation → Create.
🧱 Business Add-Ins (BADIs)
BADIs are object-oriented enhancement techniques introduced to address the limitations of procedural exits.
Based on interfaces and classes
Support multiple implementations (in case of multiple-use BADIs)
Can be filter-dependent
Types of BADIs:
Classic BADI: Managed via SE18/SE19
New BADI (Enhancement Spot): Fully embedded within the Enhancement Framework, providing enhanced flexibility and compatibility with contemporary ABAP development standards.
Example Use Case:Validating vendor master data using VENDOR_ADD_DATA BADI.
METHOD if_ex_vendor_add_data~check_data.
IF i_lfbk-bankn IS INITIAL.
MESSAGE 'Bank account number required' TYPE 'E'.
ENDIF.
ENDMETHOD.📊 Comparison: Enhancement Techniques in SAP

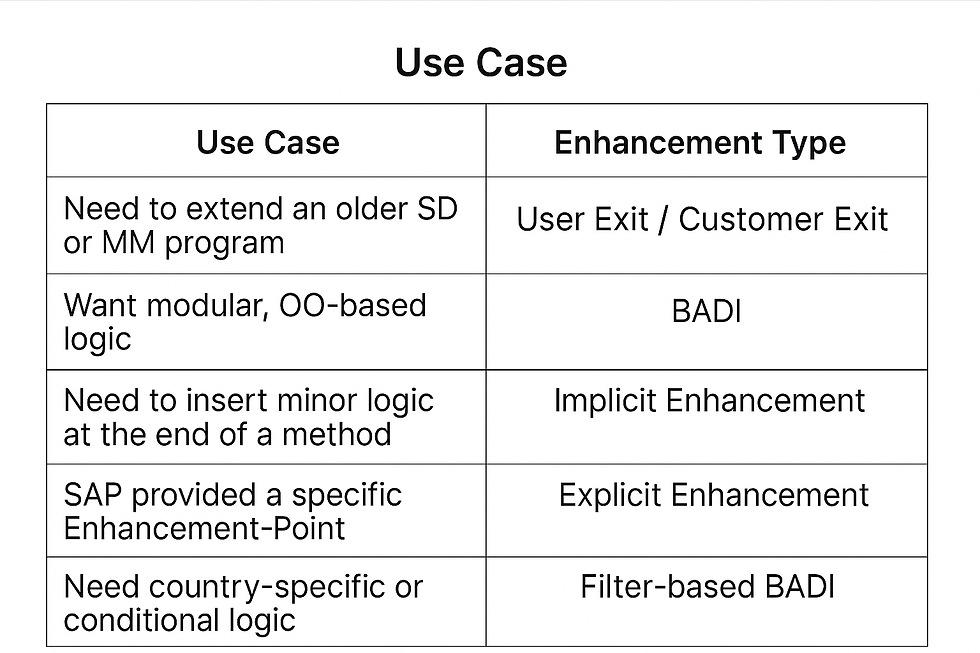
✅ When to Use Which Enhancement?
🔐 Important Tips for ABAP Developers
Never modify standard SAP code directly. Always use enhancements or the modification framework.
Use Enhancement Spot documentation to understand SAP’s intent and structure.
Combine BADIs with SE84 and debugging to find enhancement options.
Comment your enhancement implementations clearly to improve maintainability.
🧠 Final Thoughts
SAP enhancements are a powerful tool in your ABAP development arsenal. Whether you're working with legacy systems or modern S/4HANA projects, knowing when and how to use each type—User Exit, Customer Exit, BADI, or Enhancement Point—will make your code cleaner, more upgrade-safe, and easier to maintain.
By understanding the difference between explicit and implicit enhancements, and how to implement each method effectively, you’re well on your way to becoming a proficient SAP ABAP developer.
Happy Learning!
Dr. Tech
📌 FAQs
Q: What is the difference between enhancement and modification in SAP?
Enhancement is a non-intrusive way to add functionality, while modification alters SAP standard code directly.
Q: Are user exits still supported in S/4HANA?
They are largely deprecated. Use BADIs and enhancement points in modern SAP systems.
Q: How can I find enhancement options for a transaction?
Use SE84, or debug with CL_EXITHANDLER for BADIs, and explore enhancement points via SE80.
